EXAMPLE 3.4.14
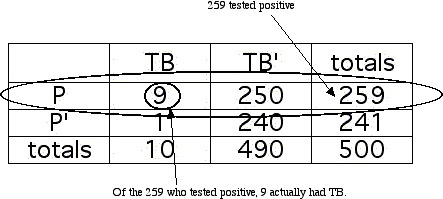
The conventional test for tuberuculosis (TB) is only about 50% accurate. Does this mean that if you test positive for TB, then the probability that you actually have TB is about .5? Suppose that the table below summarizes the results of the TB screening for a sample of 500 people. In this table, TB means "A person has tuberculosis," and P means "A person tests positive for TB." Use this information to find the probability that a person who tests positive for TB actually has the disease.

Of the 259 who tested positive, only 9 actually had TB, so
P(had TB, given tested positive for TB) = 9/259 or roughly .035.
(Also note that the data in the table shows that overall the test was about 50% accurate; out of 500 patients there were 250 false positives and 1 false negative.)