Richard Bertram

Photo credit: Devin Bittner
Academic Appointments and Honors



- Fellow of the Society for Mathematical Biology, awarded 2023
SMB Fellow Awardees
- Tam Family Professor of Mathematics, 2019-2025
- Distinguished Research Professor, awarded 2019
DRP Awardees
- Marion Bradley Brennan Professor of Mathematics, 2015-2018
- Director of Biomathematics Program, FSU, 2010-present
- Professor of Biomathematics, FSU, 2009-present
- Graduate Faculty Member, Molecular Biophysics Program,
FSU, 2001-present
- Graduate Faculty Member, Neuroscience Program,
FSU, 2005-present
Current Funding


- NIH R01 DK 080714: Four-year award for
"Microfluidic Devices for Determining Dynamics of Islets of Langerhans",
Mike Roper (PI), Richard Bertram, 2022-2026.
- NSF DMS 2324962: Three-year award for
"New Approaches for Interpreting Neural Responses to Behaviorally-Relevant Sensory Stimuli",
Richard Bertram (PI), Tom Needham, Martin Bauer, Roberto Vincis, 2023-2026.
Professional Service



Teaching Links
Current Research Interests
Activity of Pancreatic Beta-Cells
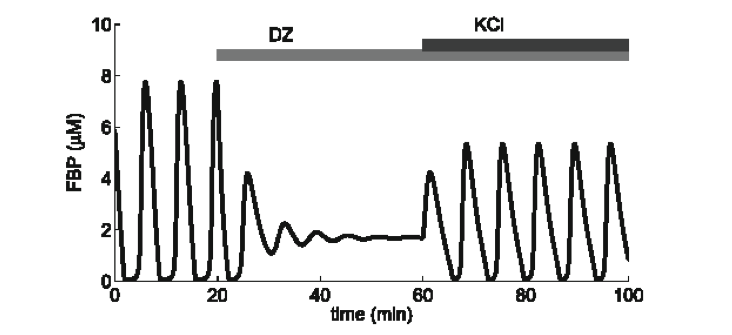
Pancreatic beta-cells are located in islets of Langerhans in the pancreas and
are the only cells in the body that secrete insulin,
a hormone that is necessary for the uptake of glucose by other cells.
Defects in beta-cell functioning lead to diabetes, which can result
in death if not treated. The release of insulin is controlled by many
physiological variables, including the cell's electrical activity,
calcium, and nucleotide concentrations. I work in the development and
analysis of mathematical models of beta-cell activity as well as
potential methods for islet syncrhonization.
The Neural Basis of Chemosensing

Humans and other animals sense their environment in a number of ways,
including responding to molecules in the air or on the tongue. This
This sensory mechanism is referred to as chemosensing. I collaborate with
two experimental labs and a number of fellow mathematicians to use
mathematical modeling and data analysis to understand how taste information
is coded in the olfactory bulb and how odor information is coded
in the gustatory cortex of the brain.
Bursting Oscillations in Excitable Cells
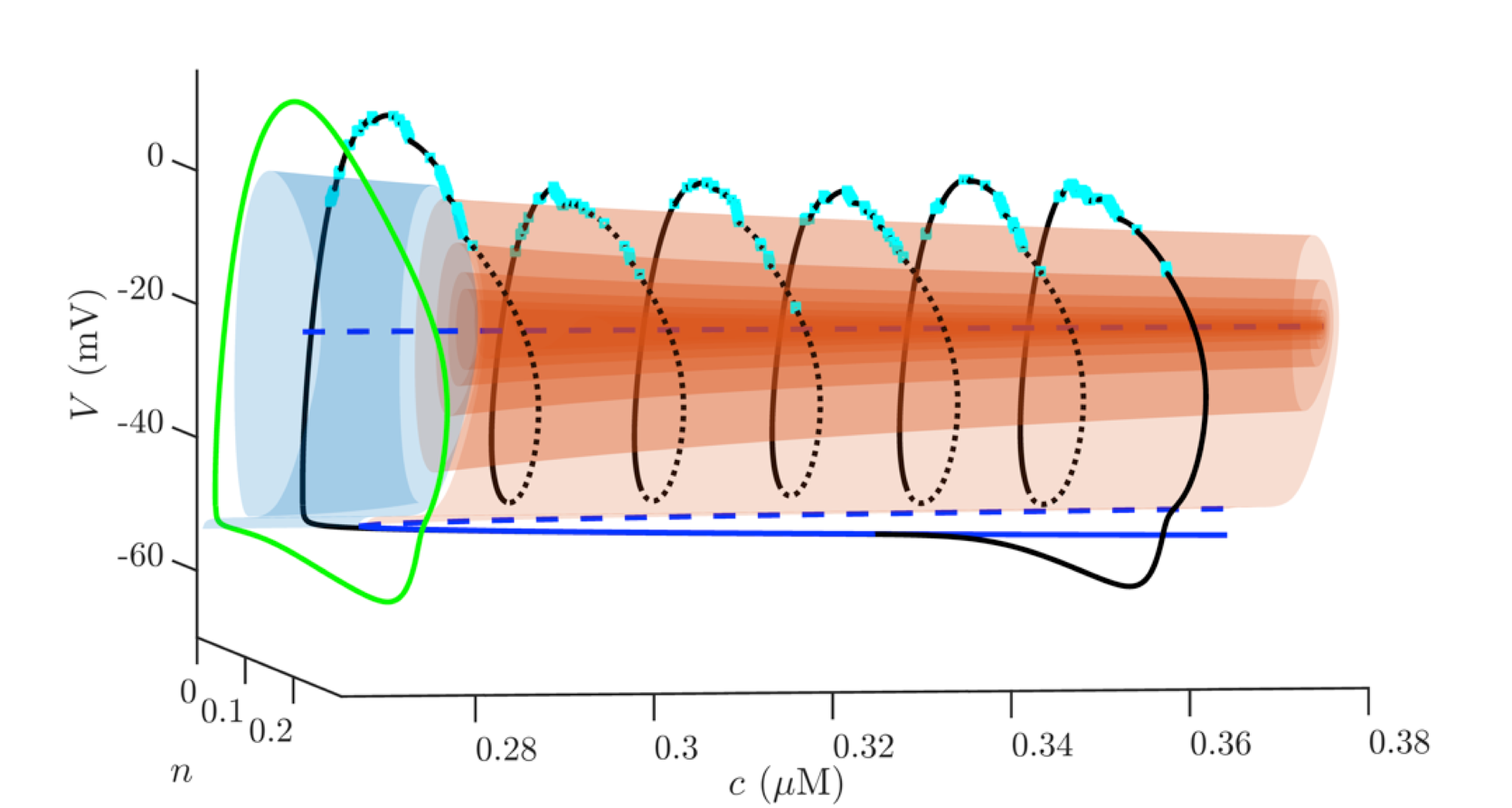
In nerve cells, information is transmitted through electrical impulses.
Electrical impulses also cause muscles to contract and endocrine cells
to secrete hormones. Quite often, impulses are generated as high-frequency
bursts, followed by periods of quiescence. This is particularly true in
endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta-cells and pituitary cells. I am
interested both in the dynamics of bursting (a mathematical topic) and in
the mechanisms by which different cells generate periodic bursts of
impulses (a biological topic).
Biological Networks

Many biological systems can be described as networks of interacting parts.
I study networks of neurons and hormone-secreting endocrine cells, as well
as gene transcription networks. This research uses techniques from network
science, statistics, and data science. Application areas include the olfactory
system, the gustatory system, hypothalamic neurons, and the
study of the disease sepsis.
Publications
Neural Models
Pancreatic Beta-Cells
Synaptic Transmission
Structural Biology
Hypothalamus and Pituitary
Neural Basis of Birdsong
Bursting Analysis
Cardiac Models
Other Topics
Lab Members
Students and Collaborators
Computer Software
Structural Biology
Hypothalamus and Pituitary
Synaptic Transmission
Pancreatic Islet
Neuron
Birdsong
Bursting Analysis
Cardiac Models
Other Topics
Biomathematics program
Video
Biophysics group
SCUBA
Music and Math
Videos
Full CV
Address
Prof. Richard Bertram
Department of Mathematics
Florida State University
Tallahassee, Fl 32306
tel.: (850)-644-7632 (IMB office)
e-mail:
rbertram@fsu.edu












